Theory
The ratio of unit weight of the
material to the unit weight of some reference material is called specific
gravity of the material. The soil solids have permeable as well as impermeable voids
of soil particles are the durability of the material. Material with high
specific gravity do not differ in gravity are likely to break down and change
their properties with time. It is importance to know the specific gravity to
ratio, porosity unit weight degree of saturation etc. it is also used to
determine the saturation line.
Application
The specific gravity is
applicable in finding out degree of saturation, specific gravity of soils is
useful in finding out the degree of saturation voids ratio and unit weight of
moist soils. The unit weight is required in calculation of pressure settlement
and stability problems in soil engineering. Specific gravity is also used in
computing particle rise of soil in sedimentation analysis.
Items required
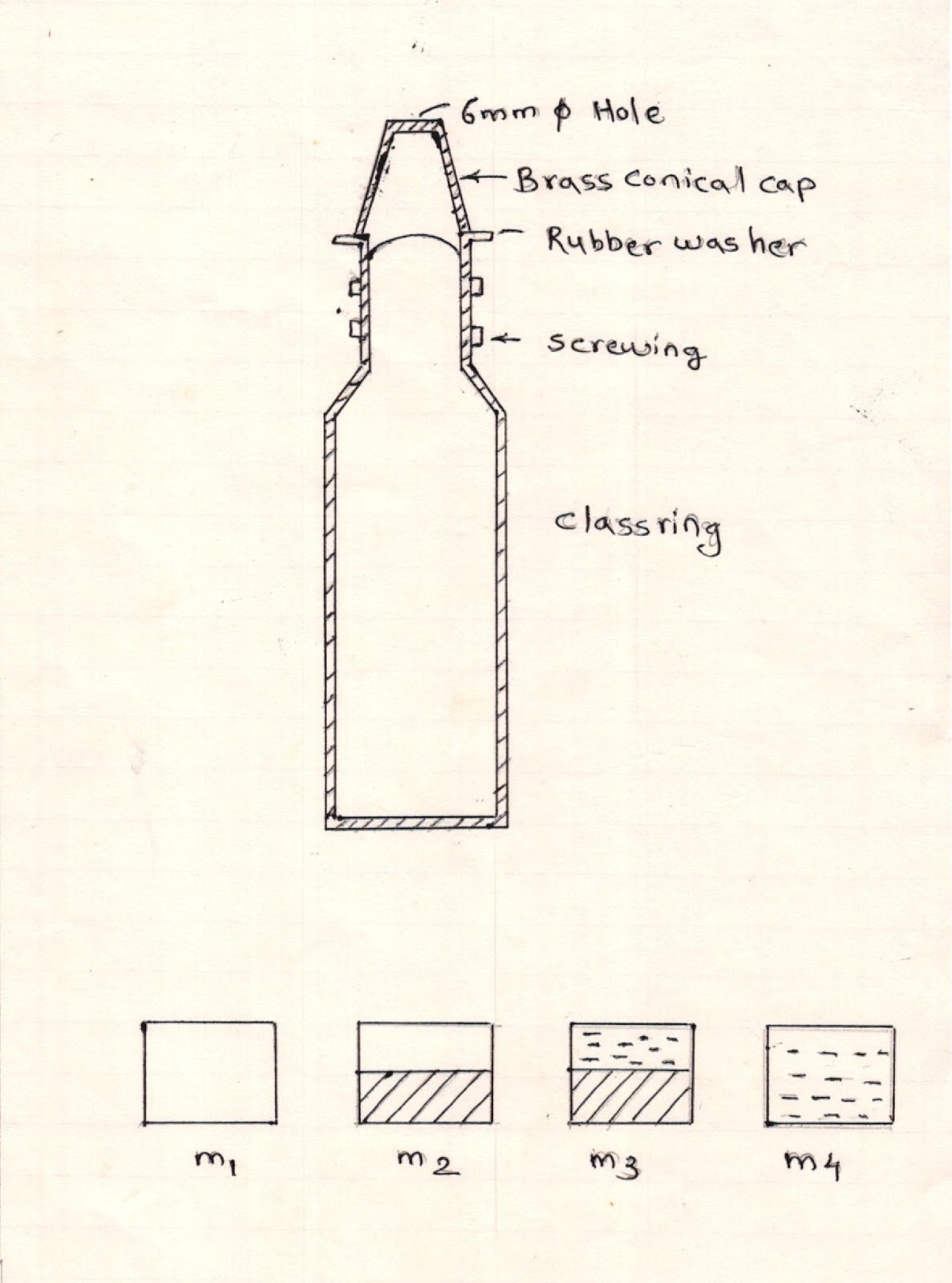
1. The pycnometer
of 500ml capacity with stoppers.
2. Balance
accurate to 0.0019
3. Oven
4. Dessicator
5. Distilled
are free water
6. I.S.
sieves 4.75mm and 2mm
7. Soil
sample passing 4.75mm and retained on 2mm sieve
8. Wash
bottole
9. Glass
rod
Diagram
Procedure
1. The
pynometers cleaned dried and weighted to the nearest 0.0019 (N1)
2. About
200gm of oven dried sample passed through 4.75mm I.S. sieve and retained on 2mm
is sieve in pycnometer and closed the stopper.
3. Weighted
the pycnometers with soil to the nearest 0.0019 (N2)
4. Add
sufficient distilled and cleared water to cover the soil in the pycnometer.
5. Stirred
the soil with glass rod to removed air.
6. Filled
the pycnometer completely with distilled water and weighted (N3)
7. Cleaned
the pycnometer and filled it completely with distilled water and its weighted
to the nearest 0.0019 (N4)
8. The
step 1 to 7 was repeated with other two pycnometer.
9. The
average specific gravity was calcultated.
Precaution
1. Mass N1,N2,N3
and N4 should be noted very carefully any error in mass gives large
discrepancy in value of specific gravity.
2. See
that the stopper is properly fitted to the pycnometer causing no leakaged
water.
3. See
that sil particals sticking to the stirring glass rod are not last.
4. For
greater accuracy the entrapped correction should be applied.
5. For
greater accuracy the entrapped air in water and soil should be removed by
vaccum pump.
6. It the
two results differ by more than 0.03 the test should be repeated.
Observation
SR.NO.
|
PARTICULAR
|
DETERMINATION NO.
|
||
SAMPLE
1
|
SAMPLE
2
|
SAMPLE
3
|
||
01
|
Pycnometer no.
|
A
|
B
|
|
02
|
Mass of Pycnometer (M1)
gms
|
442 gms
|
442 gms
|
|
03
|
Mass of Pycnometer & dry
soil (M2) gms
|
622 gms
|
614 gms
|
|
04
|
Mass of Pycnometer soil &
water (M3) gms
|
1037 gms
|
1028 gms
|
|
05
|
Mass of Pycnometer when fully
of water (M4) gms
|
930 gms
|
930 gms
|
|
Sample calculation
Specific gravity G = (M2
– M1)/(M4 – M1) – (M3 – M2)
= (622 –
442)/(930 – 442) – (1037 – 622)
= 2.74
Specific gravity G = (M2
– M1)/(M4 – M1) – (M3 – M2)
= (614 – 442)/(930 – 442) – (1028 –
514)
= 2.32
Mean = 2.74 + 2.32 / 2
= 2.53
RESULT
Specific gravity of the given
soil sample was found G = 2.53