Traffic control has been
an issue since humans put the first wheels on the first cart. The modern world
demands mobility. Cars represent the main method of mobility, but today’s
congested highways and city streets don’t move fast, and sometimes they don’t
move at all. Intelligent traffic systems (ITS), sometimes called intelligent
transportation systems, apply communications and information technology to
provide solutions to this congestion as well as other traffic control issues.
Intelligent
Transportation Systems (ITS) represent a major transition in transportation on
many dimensions. ITS is an international program intended to improve the
effectiveness and efficiency of surface transportation systems through advanced
technologies in information systems, communications, and sensors. ITS
(Intelligent Transport Systems) is a system which is designed to promote
advance technology, to ensure that the Electronic Toll Collection System (ETC)
is effective and to support safe driving. With this system, people, roads, and
vehicles use the latest information communication technology.
The intelligent
transport system (ITS) takes the first step towards meeting this challenge by
providing effective, reliable and meaningful knowledge to motorists in
time. Problems like high traffic congestion, low transportation
efficiency, low safety and endangered environment can be solved through
innovative and sophisticated ways of handling latest techniques that have
emerged in recent years in integrating information technology, electronics and
telecommunication with roads and traffic management.
Intelligent
transportation systems, or ITS, encompass a broad range of wireless and
wireline communications-based information, control and electronics
technologies. When integrated into the transportation system infrastructure,
and in vehicles themselves, these technologies help monitor and manage traffic
flow, reduce congestion, provide alternate routes to travelers, enhance
productivity, and save lives, time and money.
Intelligent transportation systems provide the tools for skilled transportation professionals to collect, analyze, and archive data about the performance of the system during the hours of peak use. Having this data enhances traffic operators' ability to respond to incidents, adverse weather or other capacity constricting events.
Intelligent transportation systems provide the tools for skilled transportation professionals to collect, analyze, and archive data about the performance of the system during the hours of peak use. Having this data enhances traffic operators' ability to respond to incidents, adverse weather or other capacity constricting events.
BENEFITS OF ITS
The investments in ITS
will help increase the benefits and efficiencies of transportation systems,
thereby reducing the need for much costlier physical expansion of systems. This
optimism is not to be confused as any kind of illusion that new infrastructure
expansion in India can be avoided altogether by resorting to ITS. Significant
expansion of infrastructure will still be needed in Indiafor a long time
to come. But including ITS in the overall development strategy of India’s
transportation system can increase the number of beneficiaries of the system,
significantly enhance the transportation-related safety which is a major
concern in most parts of India and in some cases reduce the scale of
infrastructure expansion. Thus, a realistic approach to ITS deployment
in India would consist of a balanced component of ITS as part of the
ongoing expansion of transportation system.
ITS initiatives in industrialized
countries have clearly identified a number of benefits associated with such
projects. Even though ITS projects are implemented with specific objectives
with specific benefits in mind, the overall benefits to the society may prove
to be quite substantial in many cases. For example, Toronto’s COMPASS
Freeway Traffic Management System, one of the first and successful ITS projects
in the world has been subjected to a great deal of scrutiny to evaluate its
benefits. COMPASS has been found to reduce the incident response times from 86
minutes to 30 minutes, the overall vehicle delay by 5.3 million vehicle-hours
per year, the overall emission by 3,100 tones per year and the operating costs
of commercial vehicles by $55 million per year. Cities in the United
States have reported an increase in throughout by 25% and reduction in
travel times by 25% after implementing appropriate ITS initiatives. The
following is a list of identified benefits of ITS projects :
·
Reduced rush hour congestion and delay
·
Increased safety and personal security
·
Time savings and operation efficiencies
·
Reduced fuel consumption and emissions
·
Improved customer service and reduced
frustration
·
Reduced road accidents and fatalities and
·
Enhanced economic productivity.
PRESENT DAY TRAFFIC CONTROL AND ENFORCEMENT
With the advent of new
technologies, it is necessary to update the information and implement, the know
how after carefully going through the traffic problems. At present traffic
police are regulating the traffic partially and remaining is controlled by semi
and fully automatic systems. Most of the cities in India have the
combination of manual as well as automated systems like signals, vehicle
actuated signals, electronic toll collections, CCTV, Area traffic control,
signal synchronization and coordination with local loop network.
To use or to adopt any
system for a given environment, it is important to study and analyze the
problem which helps to choose a particular method or system.
TRAFFIC PROBLEMS
Traffic congestion and
delays.
Inadequate public
transportation facilities, which run behind schedules, causing inconvenience to
public.
Inadequate road
facilities, which is not proportional to traffic growth which is due to
increase in number of vehicles with little or no space for widening or for any
change.
Prohibitive costs for
any new facilities.
High accident rates due
to varying speed of vehicles and lack of discipline among road users.
Shortage of manpower.
Increase in air
and noise pollution due to increase in number of vehicles.
Acute parking problem in
urban areas.
Absence of effective
monitoring and prevention of traffic violation.
Non-cooperation from
public for any new system or changes.
CLASSIFICATION OF ITS
Advanced public
transport system: (APTS)
APTS technologies are a
collection of technologies that increase the efficiency and
Safety of public
transportation systems and offer users greater access to information
on system operations.
The implementation of APTS technologies is transforming the
way public
transportation systems operate, and changing the nature of the
Transportation services
that can be offered by public transportation systems. The
goal is to provide
public transportation decision-makers more information to make
Effective decisions on
systems and operations and to increase travelers Convenience and rider
ship.
APTS technologies can be
organized into three broad categories that describe the
Technologies relevance
to transit applications. Each category is comprised of a
Variety of technology
choices that are available to help transport agencies and
Organizations meet
traveler’s service needs while increasing safety and efficiency.
The three APTS
technology categories are: fleet management system, travelers information
system and electronic payment system.
Advanced traveler information system: (ATIS)
Advanced travelers
information systems (ATIS), a part of new technology applications in transportation,
provide accurate and timely information that help travelers to select routes,
times of travel and travel modes. They work even better with inclusion of
geographic tourist guides and yellow pages that enable travelers to select
destinations based on proximity to other places.
Deliver data directly to
travelers, empowering them to make better choices about alternate routes or
modes of transportation. When archived, this historical data provides
transportation planners with accurate travel pattern information, optimizing
the transportation planning process.
Advanced Traffic
Management System: (ATMS)
This system can benefit
the public with improved traffic and public safety, by monitoring the flow of
traffic and making appropriate decisions in a timely manner. Additional
benefits include less fuel consumption and reduced environmental impact. They
employ a variety of relatively inexpensive detectors, cameras, and
communication systems to monitor traffic, optimize signal timings on major
arterials, and control the flow of traffic.
Automated highway
system: (AHS)
An automated highway
system (AHS) refers to a specially equipped highway lane in which vehicles are
automatically controlled; that is, the vehicles steering, brakes and throttle
are controlled by the system, not the driver. Vehicle-mounted sensors are used
to judge the vehicle's position by visual data on the lane marking. It then
uses this information to steer the vehicle. The system keeps the vehicle in the
same lane provided it senses no obstacles in the road ahead. If it detects a
slow-moving vehicle ahead, it directs the vehicle to change lanes, provided the
way is clear. Once it has overtaken the obstacle, the system returns the
vehicle to the original lane. If the next lane is occupied, the system slows
the vehicle to maintain a safe braking distance. If avehicle ahead has come to
a stop, the vehicle is smoothly brought to a stop. The AHS lanes and the
vehicles that operate on them are likely to have special sensors, computers and
communications devices to permit the automated control. To travel on an AHS, a
driver of an AHS-equipped vehicle might pull into the designated lanes, perhaps
similar to some of today’s high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lanes.
Intelligent
transportation systems offer many types of information. They may offer
real-time information about traffic conditions, such as variable message signs
(Fig:2) to warn of accidents or other delays. ITS controls the flow of traffic
via traffic signals, or by opening and closing special gated lanes that allow
commuters to access additional traffic lanes in one direction or the other,
depending on the time of day, and the direction of the heaviest commuter
traffic flow. Some applications provide fog sensors that activate road lights in
areas where heavy fog can occur and cause extremely hazardous driving
conditions. These fog sensors may also be used to send a message to a variable
message sign located before the foggy section to warn motorists of the upcoming
hazard.
They provide traffic
operators with the tools to allow quick and efficient response to accidents,
hazardous spills, and other emergencies. There are major corridors where
traffic flows are very heavy. Any small incident obstructs the flow, resulting
in huge losses in terms of fuel and time. Consequently, conducting surveillance
on corridors and identifying incidents causing problems can be useful in saving
economic losses. Surveillance systems are based on electronically operated
cameras or loop detectors embedded in pavements. Enables authorities to
identify and to respond to vehicle crashes or breakdowns with the most
appropriate and timely emergency services, thereby minimizing recovery times.
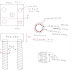
Electronic toll
collection system:
ETC is based on vehicle
roadside communication system; more precisely, it is an application of
electronic signature detection to passenger and commercial vehicle traffic for
the purpose of collecting tolls.
Here is how it works: when a vehicle
passes through the toll gate, a microwave tag (non-contact IC card) exchanges
information both ways between the gate and the vehicle to automatically
subtract the toll from, for example, a prepaid card or a bank account. This
method offers a huge increase in efficiency compared to manual toll collection,
and should reduce traffic congestion at toll-booths, save energy, and reduce
exhaust emissions(Fig:3.1)
ETC (Electronic Toll
Collection System) is a system by which drivers can pay tolls without having to
stop at a tollbooth. The collection of fees is performed electronically by way
of equipment installed in the vehicle and sensors at the toll
location.
Advanced warning
system: (AWS)
This system addresses
the present accident caused when traffic slows down abruptly due to road
conditions, forcing the driver to apply brakes and if they cannot apply brake
in advance, it may cause crash to other vehicles and at the same time vehicle
behind may crash into this vehicle. This leads to chain reaction of accidents.
The information given to the driver when the vehicles come close either from
front or back is conveyed through AWS which helps in preventing road crashes.
Vehicle Information and
Communications System: (VICS)
In this system, the
drivers are provided with real-time information on the traffic conditions via
FM multiple broadcasting, radio waves. Here the traffic personnel can take a
channel in FM band to update and inform all road users about the Traffic flow
conditions and other information like congestion, jams, roadblocks, pollution
levels etc.
Road map( fig 4.1 ) quickly shows the driver the
traffic conditions in surrounding areas..
The map shows the driver which roads are congested.
It also displays other traffic restrictions, such as expressway on-ramp
closures. The driver can use this information to select the best route by using
in-vehicle
monitor.
(Fig: 4.2) In vehicle monitor
Video
transmission:
Surveillance of
intersections, ramps and tunnels, incident detection or verification, and
replacement of traffic signal loop sensors is an increasingly popular ITS tool.
Lately, communities have been installing cameras on traffic signals to record
the license plates of cars whose drivers run a red light. All of these
applications require distance between the site where the information is
collected and the location where the information gets stored. Video
transmission that incorporates 2-way data has grown as an ITS application.
Vehicles with speed violations can be captured along with registration numbers
using this system at places like mid block, junctions, etc. Automatic detection
of unauthorized vehicles on restricted corridors and parking areas are possible,
which improves the traffic control and safety. These are some of the
applications of this system.
NECESSITY
FOR USING ITS
Provides novel
applications by smart technology.
Systematically employs
advanced technologies in the field of transportation to enhance benefits for
road users.
Improves the existing
transportation services through interconnected embedded technologies.
The mean speed can be
increased by efficiently monitoring the vehicle speeds.
Reduction in road
crashes.
Provides system to avoid
collision, accidents, and improves night vision and road alertness.
Enables the rapid
arrival of emergency vehicles during accidents to transfer the victims to
trauma care centers within the golden hour through incident management systems.
ITS IN INDIA
In India 70
State Transport Undertakings which together own and operate 1,13,000
Buses and, provide
mobility to 65 million passengers a day, across the length and
Breadth of the country.
APTS technologies along with Fleet Management Systems
can make use, to achieve
sustainable and environmental friendly transportation for
the 21stCentury. In
addition to the above technologies, institutional and market
factors also play an
important role in successful ITS deployment for enhanced
safety, mitigation of
environmental impacts of transportation systems, enhanced
energy performance, and
improved productivity.
ITS has been proved to
be the optimal solution to the enigma of building and
operating transportation
systems to meet expeditiously growing urban travel demand
in developed
countries.
The most important task
of ITS India will be the dissemination of ITS knowledge and imparting
training for new professionals. ITS India would be able to bring the
ITS expertise in the public and private sectors and academia under one
umbrella. Taking into account the political, economic and linguistic
differences in India from one region to another, the ministry of
Surface Transportation may have to take the lead in establishing such an
organization. In the Indian context, a professional body of this nature would
be expected to consist of regional units in each state with a coordinating
central body.
In 1980’s, number of
developed countries started using advanced systems to control and regulate the
traffic, accident accident prevention, parking , toll collections,
signalization and other vital tasks. This is still to develop
in India to suit our local ambience. Also the problems faced by us
are different than those in developed countries. The very first equipment to be
used in Indian environment was electronic toll collection along the newly
created expressways viz., Delhi-Noida, Ahmedabad-Mehasana, Mumbai-pune,
expressways which is functioning satisfactorily.
What we need for the
present day in India is to save the lives of innocent people from
onslaught of accidents, which is termed as “murder on wheels”. This is because
every year more than rupees 7000 crores are being spent as compensation from
authorities. Using ITS, it is possible to save the lives of the victims by
transferring them to trauma care centers within the golden hour. Almost, more
than 1% of GDP is just paid as compensation. In developed countries, a portion
of this type of amount is spent in advance to improve road, traffic and other
related conditions to prevent accidents beforehand, which are termed as “import
cost”. In India, accidents are allowed to take place and compensation is
paid later which amounts to a greater magnitude, which is termed as “export
cost”. In this direction, number of technically advanced systems are available
in the developed countries, whereas this is always a question mark in
developing countries particularly in India.
What is needed in the
present context is the mindset of policy and decision makers to use for Indian
highways and problematic locations of urban areas. What ultimately is expected
is co-operation from end user and the adaptation to the new system.
CONCLUSION
The potential of ITS
technologies in improving the efficiency of transportation sector
in Indiaappears to be very promising based on the experience of other
countries. It is understood that a national strategic ITS plan
for India is needed for the effective development and deployment of
ITS initiatives in India. A broad framework of such a plan is presented
here to generate a discussion on the topic among transportation professionals
and policy makers in India. The importance of professional cooperation in
the area of ITS between the public and private sectors and the academia is also
identified and a preliminary organizational set-up towards this end is
presented in the form of ITS India.
In India many
infrastructural projects are under construction and some are still in planning
stage. Some of the ITS technologies like AWS, ETC, fleet management, incident management
can be applied to achieve an efficient transport system. Public transport that
is almost monopolized in Indian cities can utilize ITS based technologies for
their effective operation. Since ITS technology is as old 20 years in the
world, India will have to pick up this for its updating and on par
with developed countries in modern transportation requirements.